Chest Tube Placement for Spontaneous Pneumothorax Which of the Following
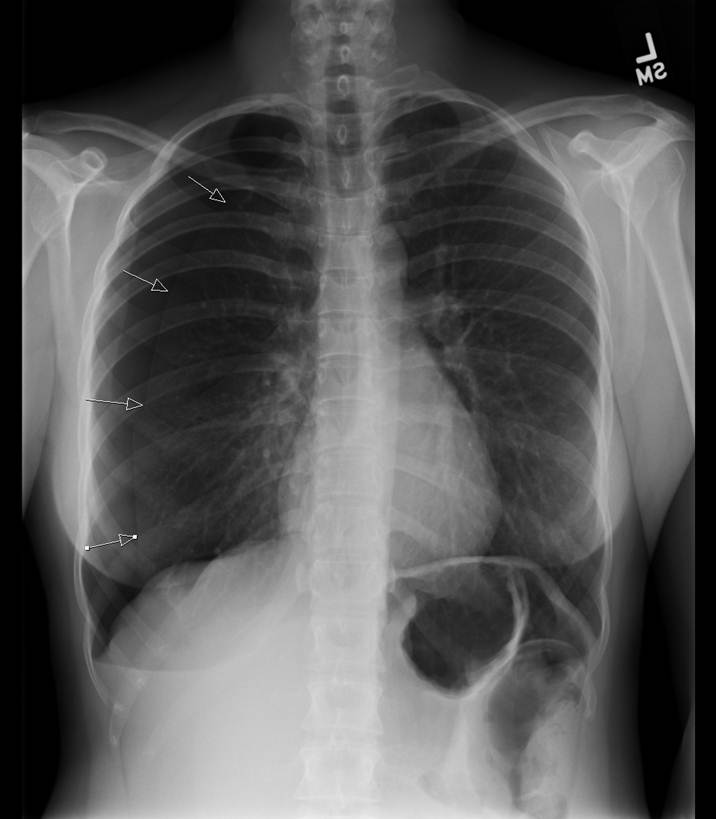
There is an approximately 20-35 right-sided pneumothorax seen which is improved from previous exam. Two previous cases have described pneumosc.

References In Pneumothorax And Chest Drain Insertion Surgery Oxford International Edition
Pigtail catheters have been used as this can potentially cause less pain.

. All of the following are indications for chest tube placement EXCEPT. Success rate of therapy was significantly higher with TD than with NA 93 CI 84 to 100 vs 67 CI 51 to 83. Chest tube insertion CTI and connection to water seal system is a common treatment modality in the first episode of Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax PSP patients.
In this respect we have come to doubt on the justification for routine postoperative chest tube placement. Typically patients who get chest tubes or pigtail catheters require. Place CT into pleural space using the finger you left inside-For pneumothorax guide the tip of the tube anteriorly and superiorly air up.
In a spontaneous pneumothorax a leak from the lung allows air to enter the negative pressure pleural space until there is no longer a pressure difference or until the leak closes 1 As the air enters the pleural space the lung collapses. There is an approximately 20-35 right-sided pneumothorax seen which is improved from previous exam. Day 1 following chest tube placement.
The primary treatment strategy for spontaneous pneumothorax at our hospital is chest tube drainage but the decision to use different types and sizes is left at the discretion of the attending surgeon and can vary from a silicone chest tube size 2124 Fr to a pigtail catheter size 1216 Fr. Routine antibiotic usage after the procedure is still discussed and is controversial. Standard methods of intercostal drainage may be unsatisfactory because of difficulty in placing an intercostal tube safely and a.
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is managed initially with observation and chest tube placement followed by surgical intervention in select cases. Tube thoracostomy may be indicated for pleural effusions associated with malignancy infection or hemothorax in the post-surgical setting. Unlike other reported cases of chest tube induced arrhythmias the bradycardia in our patient responded to resuscitative measures without removal or repositioning of the tube.
6 A larger pneumothorax or one that involves a large air leak may need a chest tube of 24F to 28F. 2 persistent pneumothorax on chest radiograph. Grasp the chest tube with a Kelly clamp tube should protrude just beyond the end of the clamp 11.
Hence no study has reported a case of symptomatic pneumorrhachis after chest tube insertion for spontaneous pneumothorax. A nurse is reviewing a care plan for a client admitted following chest tube placement for a spontaneous pneumothorax. A Spontaneous pneumothorax B Tension pneumothorax C Hemothorax Hemopneumothorax D Intercostal artery injury F Pleural effusion empyema chylothorax.
We present the case of an elderly patient who became bradycardic after chest tube insertion for spontaneous pneumothorax. 3 patient agreed to have surgery. Traditionally patients presenting with a large spontaneous pneumothorax are treated with chest tube placement and hospital admission.
28 patients or with simple needle aspiration NA. It also serves as a route to instill antibiotics post-pneumonectomy empyemas sclerosing agents pleurodesis as well as fibrinolytics DNAse andor saline complicated parapneumonic. 1 persistent air leak on day 4 after insertion of chest tube as measured by bubbling chest tube attached to an underwater seal or evidence of ongoing air leak through the ambulatory device.
There is interval placement of a right-sided chest tube with pigtail tip seen within the right lower lung field oriented downward. The patient recovered uneventfully once the air leak surrounding the tube was successfully closed at the entry wound. For this patient the chest tube was placed for spontaneous pneumothorax a common complication in cystic fibrosis.
The left lung field appears fairly clear. Placement of an apical chest tube by a posterior intercostal approach. A patient is recovering from a pneumothorax and has a chest tube present.
Which of the following interventions is appropriate. The left lung field appears fairly clear. With little currently published evidence the role of surgical pleurodesis or pleurectomy to reduce primary spontaneous pneumothorax recurrence is unclear.
12 However procedural re-expansion with a catheter or chest tube is recommended for all large pneumothoraces regardless of symptomatology or clinical stability. This study flips the current treatment dogma and suggests that a conservative approach of observation is. Apical pneumothorax due to incomplete expansion of the lung is not uncommon following thoracotomy and also occurs in some patients with recurring spontaneous pneumothorax.
Chest tube insertion was the first line of treatment in about 40 of children with a first spontaneous pneumothorax. Arrhythmia is a rare complication of tube thoracostomy. A moderate-to-large pneumothorax can usually be treated using a chest tube of 16F to 22F that is connected to a Heimlich valve which allows air to exit the chest tube but not to enter it and to a water-sealed drainage system or to a drainage system with suction applied.
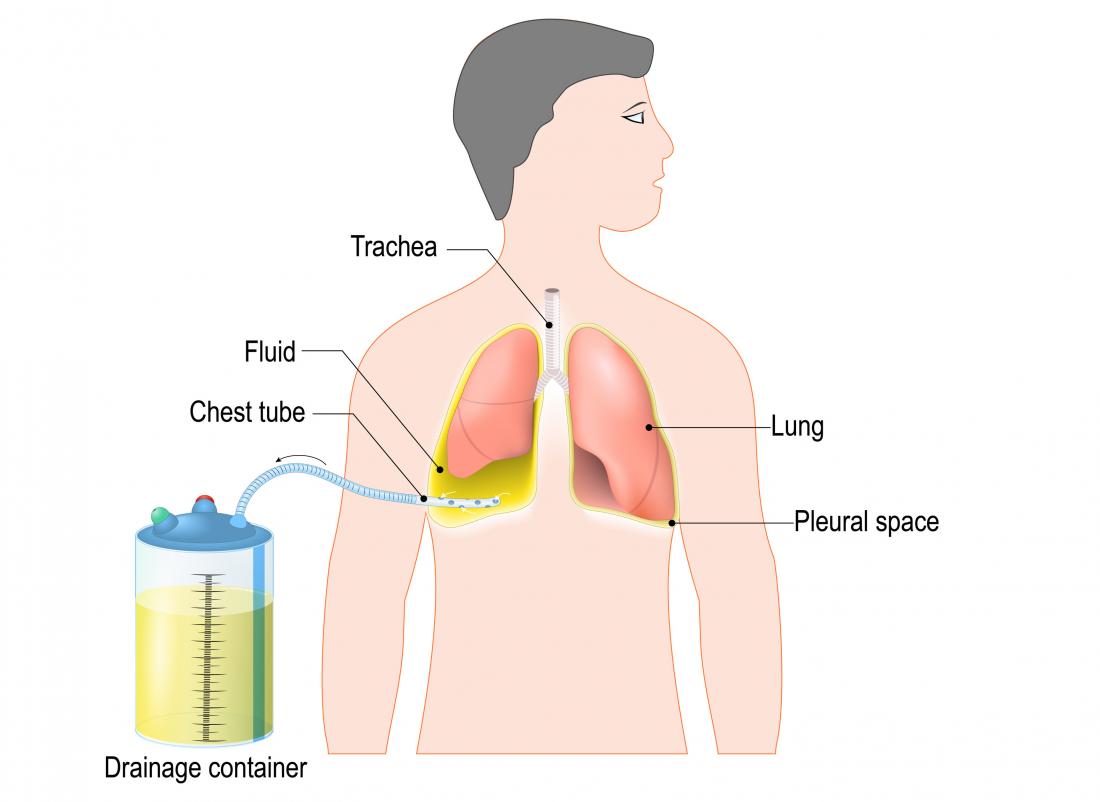
Referral for thoracic surgery occurred in the presence of all of the following. Definition Chest tube insertion is a common therapeutic procedure used to provide evacuation of abnormal collections of air or fluid from the pleural space. Which of the following is an appropriate finding when assessing the chest tube drainage system.
CHEST TUBE PLACEMENT Adult 1 I. In the first part of this study 61 patients admitted for the first episode or the first recurrence of a spontaneous pneumothorax SP were randomly treated with thoracic drainage TD. Clamp the free end of CT to prevent back flow once inserted 12.
Intermittent bubbling may be noted in the water seal chamber. 200 cc of drainage per hour is expected during recovery of a pneumothorax. Chest tube placement also called tube thoracostomy is a common procedure in daily clinical practice which is performed to drain fluid blood or air from the pleural cavity.
In present study a prospective randomized controlled trial was performed to analyze whether postoperative treatment without chest tube placement is justified in thoracoscopic wedge resection surgery for primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Tape all connections between the chest tube and drainage system. A 28-year-old man visited the.
1 More recently smaller chest tubes ie. A case of pneumoscrotum associated with a chest wall air leak following placement of a chest tube for spontaneous pneumothorax is reported. In this population the recurrence probability is established between 37 and 52 and the majority occurs in the following months.
There is interval placement of a right-sided chest tube with pigtail tip seen within the right lower lung field oriented downward. This study compares the recurrence rates.
0 Response to "Chest Tube Placement for Spontaneous Pneumothorax Which of the Following"
Post a Comment